Cutting tool geometry encompasses rake angles, clearance angles, cutting angles and nose radius. An optimum value of each of these features is required to obtain desired machining performance. However, abrupt values cannot be chosen due to various constraints. In this context, rake angle of the cutting tool can have a positive, negative or even zero value; while, clearance angle can neither be zero nor be negative. Typical values for rake angle and clearance angle is provided in the following sections.
Clearance angle cannot be zero or negative
Clearance angle of any cutting tool must have a finite positive value, usually in between +3º to +15º. A low clearance angle along with tiny edge radius is sometime desirable as it compresses feed marks on the finished surface and thus provides better quality surface. High clearance angle can make the cutting tool sharper and thus work material can be removed smoothly requiring lower cutting power. However, it reduces strength of the tool and thereby tool life degrades.
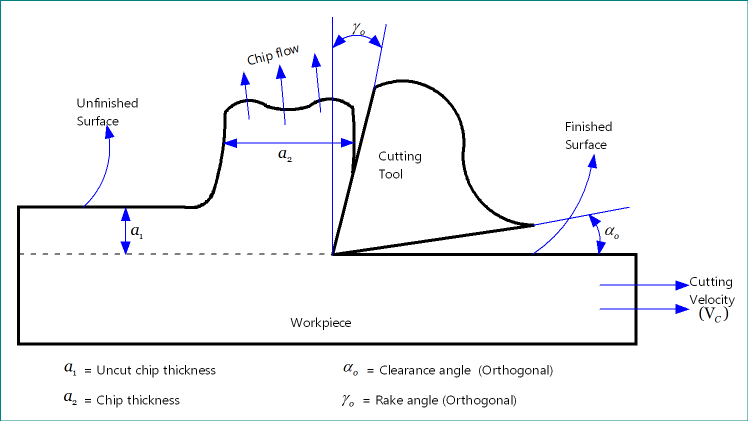
Why clearance angle cannot be zero or negative?
As shown in the schematic diagram of conventional machining, if clearance angle becomes zero then flank surface of the tool will be in physical contact with the finished surface of the workpiece. Due to the relative velocity in between these two mating surfaces, excessive heat will generate in that zone, which will lead to many undesirable problems such as degraded surface quality, burned surface, high tool wear, reduced tool life, etc. Similar problems, in severe level, will be encountered if clearance angle becomes negative. To get rid of these problems, clearance angle of the cutting tool is always kept positive, usually above +3º.
Rake angle can be positive, negative or zero
Contrary to clearance angle, rake angle of the cutting tool can have positive, negative or zero value. Usually value of rake angle varies in between –30º to +30º. A negative rake provides a stronger tool tip but increases shear deformation, chip thickness, cutting force and power consumption. On the other hand, a positive rake offers sharp cutting edge and thus helps in reducing cutting force and power requirement. However, tool life degrades sharply because of thin tool tip. A zero rake provides an intermediate result. Regarding this, you may read the following articles.