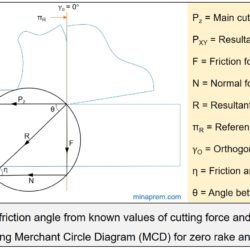
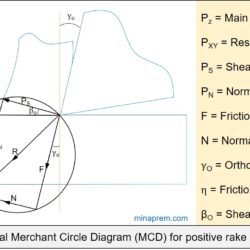
Find out shear force from given cutting force, thrust force and shear angle
Question: In an orthogonal cutting operation shear angle = 11.31°, cutting force = 900 N and thrust force = 810 N. What will be the shear force? [ESE 2014] Solution: With the help of Merchant Circle Diagram (MCD), this problem can be solved easily. A typical MCD for positive rake angle is shown below. Here in the question, the main cutting force (PZ) and thrust force (PXY) for an orthogonal