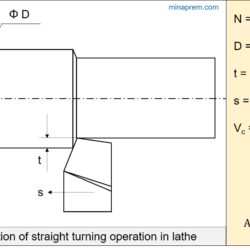
Determine principal cutting edge angle for equal side and orthogonal rake angles
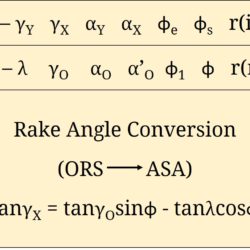
Question: In a single point turning tool, the side rake angle and orthogonal rake angle are equal. φ is the principal cutting edge angle and its range is 0° ≤φ≤ 90°. The chip flows in the orthogonal plane. Determine the value of φ. [GATE 2008] Answer: Although in majority of the analysis for straight turning, it is assumed that the chip is flowing in orthogonal direction, but actually chip flow