Normal Rake System (NRS) differs from the Orthogonal Rake System (ORS) due to the presence of inclination angle in cutting tool. Inclination angle (λ) is defined as the angle of inclination of principal cutting edge from the reference plane (πR) and measured on cutting plane (πC). Therefore if inclination angle (λ) of the cutting tool becomes zero then ORS and NRS will be exactly same.
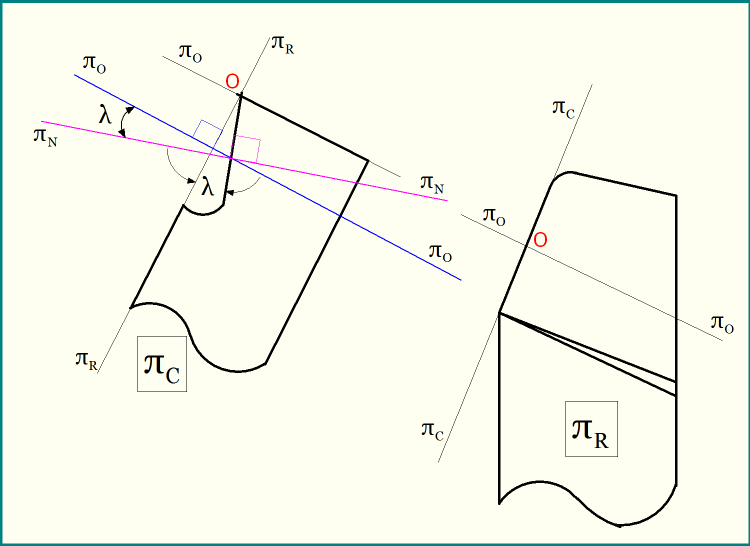
The orthogonal plane (πO) used in ORS system is perpendicular to both cutting plane (πC) and reference plane (πR). This is irrespective of the orientation of principal cutting edge. Whereas, normal plane (πN) used in NRS system is perpendicular to the principal cutting edge. Since the angle between the cutting plane and principal cutting edge (when measured on reference plane) is called inclination angle, the angle between orthogonal plane (πO) and normal plane (πN) is also equal to inclination angle (λ).
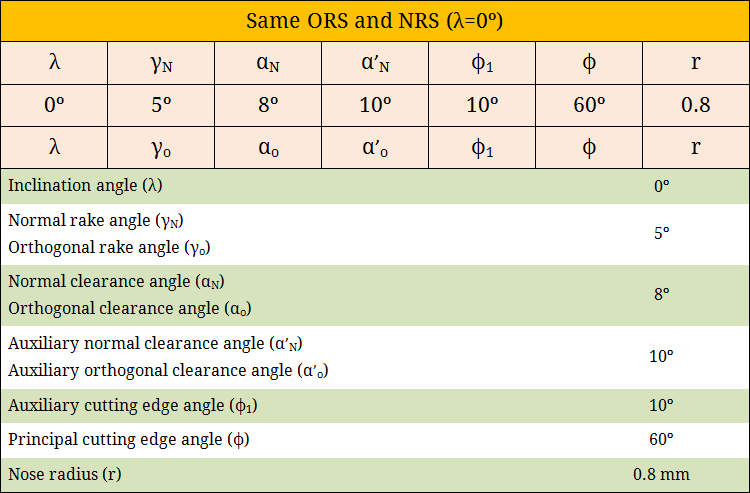
Therefore, if λ = 0º, then orthogonal plane (πO) will merge with normal plane (πN) and the same will be perpendicular to both cutting plane (πC) and reference plane (πR). Moreover, a zero inclination angle indicates that rake surface coincides with reference plane along the principal cutting edge. In such case, principal cutting edge will also be the Master Line for rake. The following image illustrates the zero inclination angle condition and the same values for corresponding angles in ORS and NRS.
References
- Book: Principles of Mechanical Engineering by S. Singh (S. Shand).
- Book: Machining and Machine Tools by A. B. Chattopadhyay (Wiley).
- Book: Metal Cutting: Theory And Practice by A. Bhattacharya (New Central Book Agency).